Lactate Threshold Testing for Beginners

With the New Year behind us, many of us are either getting back into our respective training plans and programs or creating new ones for the upcoming race season. When creating a training plan or even just following one (let’s be honest we’ve all found one online and just jumped into it) it can be difficult to measure your progression before race day. Even worse than that, we’ve all hit the wall during the offseason and thought: Why am I even doing this? Is this helping?Am I doing what I should be? What if I get to the race and I’m not ready?
We all go through it. You’re not alone! Something that I implement into my programs and my athlete’s programs are frequent lactate threshold (LH) testing. Frequent testing can provide a numerical value to your training progression which can ultimately boost your motivation and keep you going through a cold winter or long offseason.
For those who don’t know, when you use your body’s muscles for exercise or physical activity, the product of muscular metabolism (meaning the breaking down of muscles for bioenergetic purposes during high intensity/extended duration exercise) is called lactate1. The reason your muscles can continue to contract during extended periods of exercise is that while lactate accumulates in the blood during training, your liver is working to metabolize the lactate in the blood. Unfortunately, after your muscles are not provided an adequate volume of oxygen for long enough (the body moves to its anaerobic energy systems, ex. phosphagen and glycolytic) your muscles start to produce lactate faster than it can be metabolized by your liver. The point at which your lactate production and lactate metabolism are in equilibrium is known as your Lactate Threshold (LH) or Maximal Lactate Steady State (MLSS)2. Basically, there is a point (usually a speed like 5:30 min./mile pace for example) where your muscles start to become extremely fatigued and can only maintain a speed/rate for a short time. So, ideally, if you are able to stay at a speed/pace below your LH speed/pace you should be able to maintain that speed/pace for quite a while (i.e. endurance events).
Now, knowing what an LH is and somewhat of how it works, we can talk about LH testing and how to include it in your training plan. Training to increase your LH usually includes various speed or high-intensity training during some of your swim, bike, and run sessions. Increasing your LH means being able to run farther faster. Most amateur triathletes, who are trying to increase their LH, include one key or high-intensity session for each of the three sports per week. These sessions tend to be shorter than endurance sessions due to their high energy demand from the body. Example: a 30-minute sprint interval run vs. a 1-hour aerobic endurance run. The 30-minute sprint interval run requires more use of the anaerobic energy systems and therefore helps to increase your LH. Since these workouts require so much from the body and thus require more recovery to allow the muscles to rebuild, I advise not scheduling two of these workouts on the same day. This should allow enough time for proper recovery between sessions.
LH testing can be done in a number of ways. There are a bunch of tests out there (just Google LH testing and you’ll see) so if the ones I talk about here don’t sound that great, then you have options. The tests that I have included below are the tests that I use with my athletes and myself and I have had success with them in the past. I advise my athletes to test before starting a training plan and about every three weeks during training. I feel that three weeks is enough time to see results from the tests completed at the beginning of the plan. However, testing does not always have to be in training. I also schedule training races for my athletes so that they can use these races as their tests (since you are most likely pushing yourself close to the maximum effort during a race anyway). When I schedule LH tests, I tend to use them in place of the high-intensity session of that particular sport that week. For example, if I have a 30-minute sprint interval session scheduled for Tuesday and that is my high-intensity run session for the week, I will replace this session with the 6-minute run test. I do this because the test will require maximum effort so even if you are only running at maximum effort for 6-minutes, you will still achieve about the same training effect as you would have during your usual high-intensity session.
If the training program that you are using is well planned and executed while allowing for proper recovery between sessions, then your LH should increase. If you see a decrease, then you may be overtraining and not providing your body adequate recovery through nutrition and rest. You might also not be pushing yourself hard enough during your high-intensity sessions. Good news though! These are easy fixes and can be season-saving (in the case of overtraining) if caught early (another reason why I test my athletes about every three weeks).
I hope that at least some of this information made sense and helps you during your next training block or plan. Recap: Most amateur triathletes include one high-intensity training session for each sport per week that is designed to increase your LH. Training sessions designed to increase your LH tend to be shorter in duration than endurance sessions. If in training, your LH decreases, you should reevaluate your plan and try to find where you went wrong. There are many LH tests out there and you should find the one(s) that work best for you. Lactate threshold testing is a great way to track your progress and stay motivated through training all the way through to race day and can be incorporated into your plan pretty easily. Happy training and good luck this race season!
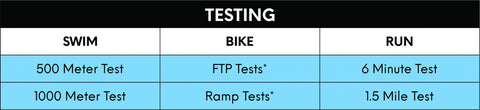
+*FTP and Ramp tests can be completed using a training software through either a power meter or power trainer (ex. Zwift, Trainer Road, Kinetic, etc.)
SWIM
500 Meter Test
Example:
500 m Test
200 m Cool Down
300 m Warm-Up
1000 m Test
200 m Cool Down
BIKE
FTP Tests: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of these tests is to determine your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) as well as your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. FTP can be used throughout your training in a variety of ways. Some examples include to create workouts, to help prevent overtraining, and to provide a numerical value to your baseline fitness so that you may be able to track your progression through the training program. FTP tests can be performed through fitness and training apps such as Zwift, Trainer Road, and Kinetic. To use these apps, you must either have access to a smart trainer or power meter of some kind. Once you are setup and ready to go with the app or program, you can then start your test which is guided by the app. FTP tests are considered to be fairly accurate and should be prioritized over Ramp tests.Ramp Tests: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of these tests is to determine your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) as well as your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. FTP can be used throughout your training in a variety of ways. Some examples include to create workouts, to help prevent overtraining, and to provide a numerical value to your baseline fitness so that you may be able to track your progression through the training program. Ramp tests can be performed through fitness and training apps such as Zwift, Trainer Road, and Kinetic. To use these apps, you must either have access to a smart trainer or power meter of some kind. Once you are setup and ready to go with the app or program, you can then start your test which is guided by the app. Ramp tests are considered to be less accurate than FTP tests, however, they are also considered to be easier to complete.
RUN
6 Minute Test: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of this test is to record your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. These values can be used throughout your training plan to create workouts and evaluate your progression. To correctly perform this test, you will need a flat track or stretch of land to run on, a heart rate monitor, and a fitness watch that can record the information from the test for review later. During the test it is very important that you push yourself to the maximum effort you can sustain for 6 minutes. An example of the test can be seen below.1.5 Mile Test: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of this test is to record your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. These values can be used throughout your training plan to create workouts and evaluate your progression. To correctly perform this test, you will need a flat track or stretch of land to run on, a heart rate monitor, and a fitness watch that can record the information from the test for review later. During the test it is very important that you push yourself to the maximum effort you can sustain for 1.5 miles. An example of the test can be seen below.
Cool Down: 10 minutes
1 Hargreaves, M. (2000). Skeletal Muscle Metabolism During Exercise In Humans. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 27(3), 225–228. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03225.x
2 Faude, O., Kindermann, W., & Meyer, T. (2009). Lactate Threshold Concepts. Sports Medicine, 39(6), 469–490. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200939060-00003

With the New Year behind us, many of us are either getting back into our respective training plans and programs or creating new ones for the upcoming race season. When creating a training plan or even just following one (let’s be honest we’ve all found one online and just jumped into it) it can be difficult to measure your progression before race day. Even worse than that, we’ve all hit the wall during the offseason and thought: Why am I even doing this? Is this helping?Am I doing what I should be? What if I get to the race and I’m not ready?
We all go through it. You’re not alone! Something that I implement into my programs and my athlete’s programs are frequent lactate threshold (LH) testing. Frequent testing can provide a numerical value to your training progression which can ultimately boost your motivation and keep you going through a cold winter or long offseason.
For those who don’t know, when you use your body’s muscles for exercise or physical activity, the product of muscular metabolism (meaning the breaking down of muscles for bioenergetic purposes during high intensity/extended duration exercise) is called lactate1. The reason your muscles can continue to contract during extended periods of exercise is that while lactate accumulates in the blood during training, your liver is working to metabolize the lactate in the blood. Unfortunately, after your muscles are not provided an adequate volume of oxygen for long enough (the body moves to its anaerobic energy systems, ex. phosphagen and glycolytic) your muscles start to produce lactate faster than it can be metabolized by your liver. The point at which your lactate production and lactate metabolism are in equilibrium is known as your Lactate Threshold (LH) or Maximal Lactate Steady State (MLSS)2. Basically, there is a point (usually a speed like 5:30 min./mile pace for example) where your muscles start to become extremely fatigued and can only maintain a speed/rate for a short time. So, ideally, if you are able to stay at a speed/pace below your LH speed/pace you should be able to maintain that speed/pace for quite a while (i.e. endurance events).
Now, knowing what an LH is and somewhat of how it works, we can talk about LH testing and how to include it in your training plan. Training to increase your LH usually includes various speed or high-intensity training during some of your swim, bike, and run sessions. Increasing your LH means being able to run farther faster. Most amateur triathletes, who are trying to increase their LH, include one key or high-intensity session for each of the three sports per week. These sessions tend to be shorter than endurance sessions due to their high energy demand from the body. Example: a 30-minute sprint interval run vs. a 1-hour aerobic endurance run. The 30-minute sprint interval run requires more use of the anaerobic energy systems and therefore helps to increase your LH. Since these workouts require so much from the body and thus require more recovery to allow the muscles to rebuild, I advise not scheduling two of these workouts on the same day. This should allow enough time for proper recovery between sessions.
LH testing can be done in a number of ways. There are a bunch of tests out there (just Google LH testing and you’ll see) so if the ones I talk about here don’t sound that great, then you have options. The tests that I have included below are the tests that I use with my athletes and myself and I have had success with them in the past. I advise my athletes to test before starting a training plan and about every three weeks during training. I feel that three weeks is enough time to see results from the tests completed at the beginning of the plan. However, testing does not always have to be in training. I also schedule training races for my athletes so that they can use these races as their tests (since you are most likely pushing yourself close to the maximum effort during a race anyway). When I schedule LH tests, I tend to use them in place of the high-intensity session of that particular sport that week. For example, if I have a 30-minute sprint interval session scheduled for Tuesday and that is my high-intensity run session for the week, I will replace this session with the 6-minute run test. I do this because the test will require maximum effort so even if you are only running at maximum effort for 6-minutes, you will still achieve about the same training effect as you would have during your usual high-intensity session.
If the training program that you are using is well planned and executed while allowing for proper recovery between sessions, then your LH should increase. If you see a decrease, then you may be overtraining and not providing your body adequate recovery through nutrition and rest. You might also not be pushing yourself hard enough during your high-intensity sessions. Good news though! These are easy fixes and can be season-saving (in the case of overtraining) if caught early (another reason why I test my athletes about every three weeks).
I hope that at least some of this information made sense and helps you during your next training block or plan. Recap: Most amateur triathletes include one high-intensity training session for each sport per week that is designed to increase your LH. Training sessions designed to increase your LH tend to be shorter in duration than endurance sessions. If in training, your LH decreases, you should reevaluate your plan and try to find where you went wrong. There are many LH tests out there and you should find the one(s) that work best for you. Lactate threshold testing is a great way to track your progress and stay motivated through training all the way through to race day and can be incorporated into your plan pretty easily. Happy training and good luck this race season!

+*FTP and Ramp tests can be completed using a training software through either a power meter or power trainer (ex. Zwift, Trainer Road, Kinetic, etc.)
SWIM
500 Meter Test
Example:
500 m Test
200 m Cool Down
300 m Warm-Up
1000 m Test
200 m Cool Down
BIKE
FTP Tests: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of these tests is to determine your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) as well as your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. FTP can be used throughout your training in a variety of ways. Some examples include to create workouts, to help prevent overtraining, and to provide a numerical value to your baseline fitness so that you may be able to track your progression through the training program. FTP tests can be performed through fitness and training apps such as Zwift, Trainer Road, and Kinetic. To use these apps, you must either have access to a smart trainer or power meter of some kind. Once you are setup and ready to go with the app or program, you can then start your test which is guided by the app. FTP tests are considered to be fairly accurate and should be prioritized over Ramp tests.Ramp Tests: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of these tests is to determine your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) as well as your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. FTP can be used throughout your training in a variety of ways. Some examples include to create workouts, to help prevent overtraining, and to provide a numerical value to your baseline fitness so that you may be able to track your progression through the training program. Ramp tests can be performed through fitness and training apps such as Zwift, Trainer Road, and Kinetic. To use these apps, you must either have access to a smart trainer or power meter of some kind. Once you are setup and ready to go with the app or program, you can then start your test which is guided by the app. Ramp tests are considered to be less accurate than FTP tests, however, they are also considered to be easier to complete.
RUN
6 Minute Test: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of this test is to record your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. These values can be used throughout your training plan to create workouts and evaluate your progression. To correctly perform this test, you will need a flat track or stretch of land to run on, a heart rate monitor, and a fitness watch that can record the information from the test for review later. During the test it is very important that you push yourself to the maximum effort you can sustain for 6 minutes. An example of the test can be seen below.1.5 Mile Test: This test is to be performed alone. Training with others can affect the accuracy of your results since training with other athletes inadvertently causes most athletes to push themselves harder than they would normally. The point of this test is to record your maximum heart rate and lactate threshold. These values can be used throughout your training plan to create workouts and evaluate your progression. To correctly perform this test, you will need a flat track or stretch of land to run on, a heart rate monitor, and a fitness watch that can record the information from the test for review later. During the test it is very important that you push yourself to the maximum effort you can sustain for 1.5 miles. An example of the test can be seen below.
Cool Down: 10 minutes
1 Hargreaves, M. (2000). Skeletal Muscle Metabolism During Exercise In Humans. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 27(3), 225–228. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03225.x
2 Faude, O., Kindermann, W., & Meyer, T. (2009). Lactate Threshold Concepts. Sports Medicine, 39(6), 469–490. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200939060-00003
SEE WHAT CUSTOM APPAREL LOOKS LIKE

GEAR UP
MORE FROM THE BLOG

The Essential Reading List for Aspiring Triathletes

The most challenging competitions in the world: A guide to the toughest races on the planet
How to Keep Young Athletes Motivated in Their Training Program
Let’s admit it: many athletes struggle to find motivation for their training. Experts from the University of London and the National...

How To Adapt Your Training When Things Go Wrong
It is pretty easy nowadays to find the perfect training plan online for whatever event you have coming up. The...



